200以上 yield strength vs density graph 334216-Yield strength vs density graph
Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofThe specific strength is a material's strength divided by its density It is also known as the strengthtoweight ratio or strength/weight ratio or strengthtomass ratio In fiber or textile applications, tenacity is the usual measure of specific strength The SI unit for specific strength is Pa m3/kg, or N·m/kg, which is dimensionally equivalent to m2/s2, though the latter form is rarely used Specific strength has the same units as specific energy, and is related to the maximum specificMain Difference – Yield Strength vs Tensile Strength In materials engineering, yield strength and tensile strength are two properties that can be used to characterize a material The graph below shows the stressstrain curve for a typical ductile material such as steel
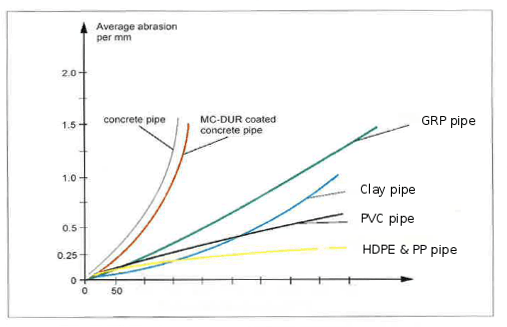
Polyethylene Pipe Pe Hdpe Properties And Types Of Pe100 Pipe
Yield strength vs density graph
Yield strength vs density graph-The StressStrain Graph The strength of a material is determined by a tensile test, a test that requires the material to be mercilessly pulled from its two ends The relationship between the stress to which it is subjected and the strain it consequently suffers can be limned by a graph called the stressstrain curveFracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occurs Stiffness is how a component resists elastic deformation when a load is applied Hardness is resistance to localized surface deformation The strength of a material can refer to yield strength, ultimate strength, or fracture strength


Materials Used In Automotive Manufacture And Material Selection Using Ashby Charts
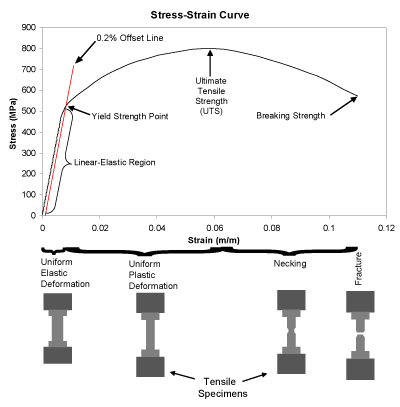
Tensile tests are used to determine the modulus of elasticity, elastic limit, elongation, proportional limit, reduction in area, tensile strength, yield point, yield strength and other tensile properties The main product of a tensile test is a load versus elongation curve which is then converted into a stress versus strain curveMetal yield strength chart lewisburg fastener specifications astm a193 a3 parison of ductile iron vs steel ultimate tensile strength uts mechanical properties of metals weld guru Yield Strength Mechanics Of Materials Ers EdgeMetal Strength Chart Mechanical Properties Of Diffe Grades And Alloys CnclathingIs Platinum The Strongest Metal QuoraYield Strength Mechanics Of Materials ErsYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is
TENSILE YIELD STRENGTH OF STEEL CHART Tensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room Temperature Material Yield Strength Tensile Strength % ElongUltimate tensile strength is often shortened to "tensile strength" or even to "the ultimate" If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals)Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?
We have collected a number of charts detailing applications and properties for some of the most commonly used ceramic materials While the data in these charts is, in most cases, typical of what you will find from ceramic component suppliers, it is only intended to be a general point of reference and should not be used for material selection or specificationIn brittle materials, tensile strength is reached with minimal or no yield Tensile strength is usually of a higher numerical value than the yield strength of a particular material The tensile strength of a material can be ascertained with 100% accuracy However, yield strength has to be estimated for most materials Yield and tensileTENSILE YIELD STRENGTH OF STEEL CHART Tensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room Temperature Material Yield Strength Tensile Strength % Elong



Mechanical Testing 3d Printed Parts Results And Recommendations Engineerdog


Q Tbn And9gcrw3nozcnyh4bwqfeukau 7r12lvur1bwxh Tnmfcd2pb2w95tx Usqp Cau
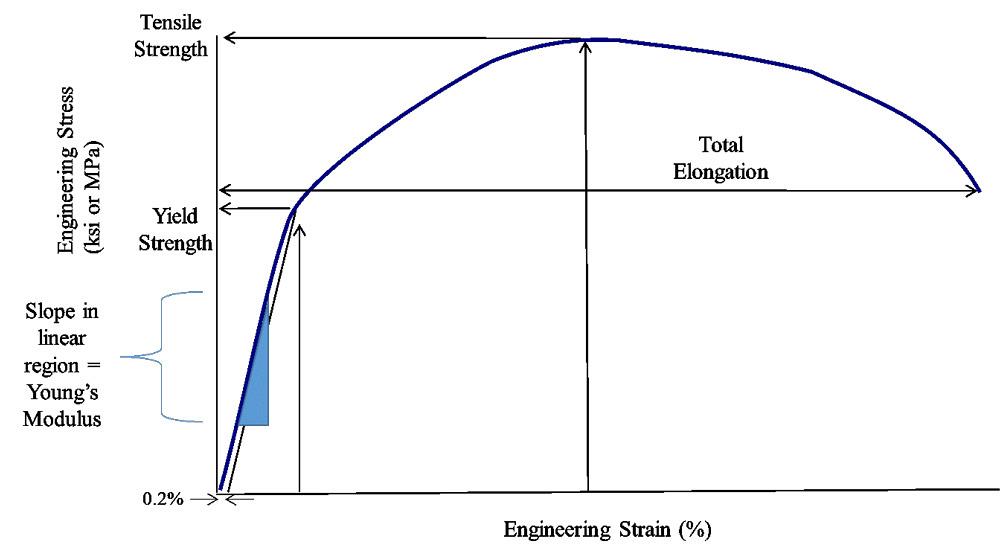
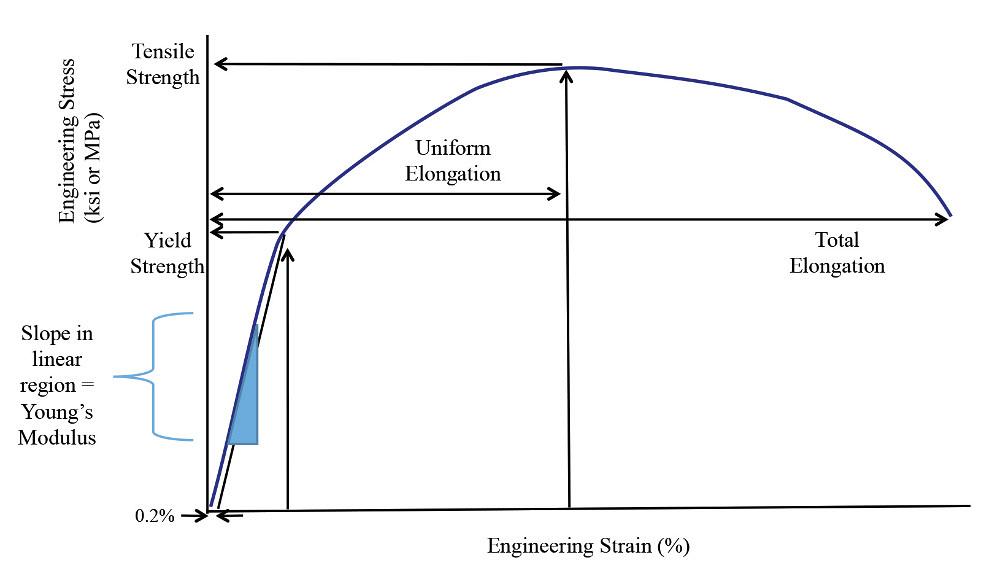
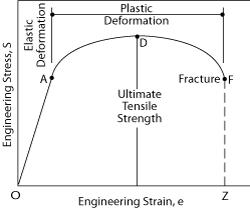
Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"For static applications, the yield strength is the more important design constraint as per industry standard design practices;To find yield strength, the predetermined amount of permanent strain is set along the strain axis of the graph, to the right of the origin (zero) It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point (D) Yield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials



Extraordinary Tensile Strength And Ductility Of Scalable Nanoporous Graphene Science Advances


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf
Use our interactive properties table below to explore by property group, sort, or compare two or more plastic materials Also, you may want to use our Plastic Material Selection Guide or Interactive Thermoplastics Triangle to assist with the material selection process based on your application requirements For chemically resistant plastic, view our Chemical Resistance of Plastics chartMetal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength, Tensile Strength, Yield Strength Metals & Materials / 5 minutes of reading Recently we've been getting a lot of inquiries from readers about mechanical property tables for various metals, such as the shear strength, tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of steel, etcStrength Properties 12–3 Panel Products 12–3 Plywood 12–3 Oriented Strandboard (OSB) 12–4 Particleboard 12–4 Hardboard 12–4 MediumDensity Fiberboard 12–5 Timber Elements/Structural Composite Lumber 12–5 GluedLaminated Timber 12–5 Structural Composite Lumber 12–6 Wood–Nonwood Composites 12–7 Wood–Plastic Composite 12–7



Extraordinary Tensile Strength And Ductility Of Scalable Nanoporous Graphene Science Advances


Http Users Fs Cvut Cz Libor Benes Vyuka Engineeringmaterials 2 Materials Charts 10 Pdf
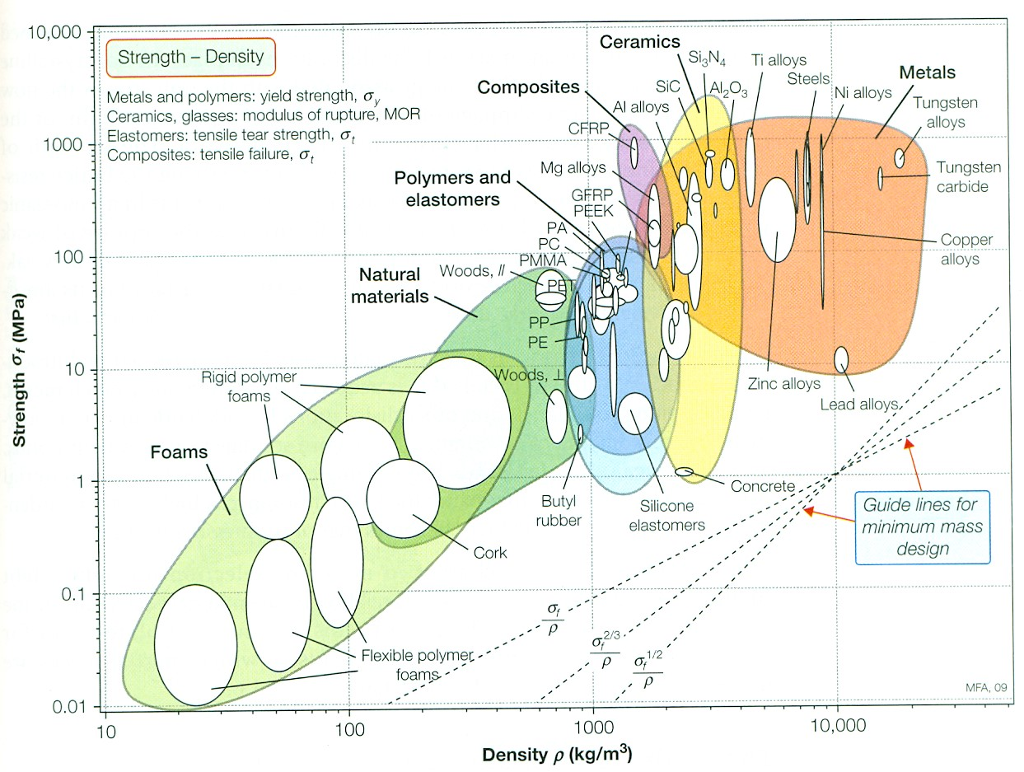
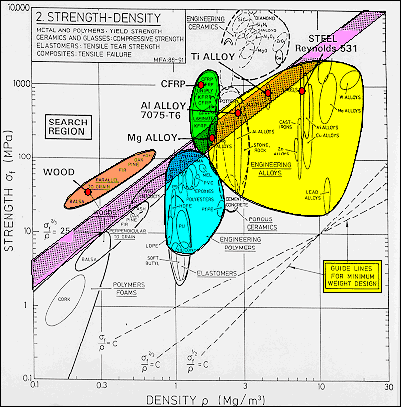
Offset yield strength is the stress that will cause a specified amount of permanent strain (typically 02 percent) It is found by drawing a line that crosses the X (strain) axis at 0002 and runs parallel to the stressstrain line (slope = E) The point where this line intersects the stressstrain curve is the offset yield pointThe yield strength, tensile strength and elastic modulus was provided for each material From this data as well the measured dimensions the specific yield strength, tensile strength and modulus were calculated The results of these calculations show that in general the metal specimen have the highest density, the ceramic sample had a relativelyGeneral Information Strength measures the resistance of a material to failure, given by the applied stress (or load per unit area) The chart shows yield strength in tension for all materials, except for ceramics for which compressive strength is shown (their tensile strength being much lower)


Civl 1101
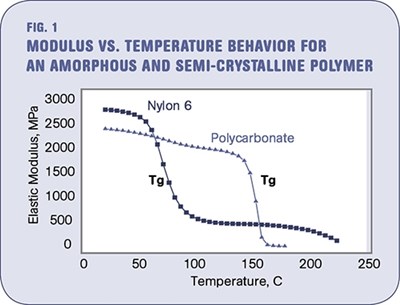


The Effects Of Temperature Plastics Technology
Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange For more information and source, see on this link https//engineeringstackexchangecomStrength of Metals SI Units Strength of Metals Imperial Units Example Strength of Copper at 100 o C As indicated in the first figure the strength of copper is reduced to approximately 95 % at 100 o C With an Ultimate Tensile Strength σ u of 2 MPa for copper the strength is reduced to 095 (2 MPa) = 9 MPaInquiry@TheGriffNetworkcom Mon – Fri 0am – 500pm EST Facebookf Twitter Youtube Linkedin Yield Tables For Film LPDE (Density 092) MICRON MIL G/SQ M G/MSF LBS/MSF SQ INCH/LB 25 1 230 47 36 15 331 68 2122 50 2 460 94 63 25 580 119 75 3 690 Yield Tables for Film Read More »


New Metal Alloy Has Highest Strength To Weight Ratio Of Any Metal



Polyethylene Pipe Pe Hdpe Properties And Types Of Pe100 Pipe
Curve Yield strength is assumed to be the maximum stress observed in each stressstrain diagram and the strain corresponding to the yield strength is the yield strain Stresscontrolled tensiontension fatigue tests were performed at 215 C The ratio of the minimum cyclic stress and the maximum cyclic stress, ie, the Rratio, was 01In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strainIt is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing)These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's modulus, the yield strengthWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement



Powder Metallurgy Engineering Properties Pickpm Com



The Mechanical Properties Of Aluminum Aluminium Guide Com
However, the ultimate strength can be useful for certain applications that call for it 6061 aluminum alloy has a yield tensile strength of 276 MPa ( psi), and an ultimate tensile strength of 310 MPa ( psi)Yield strengths range from 110 ksi through 140 ksi, but we can temper it to other strength levels When compared with standard 4140 heat treated to the same tensile and yield strengths, 4140HW achieves significantly higher toughness, as measured by impact strength (see Figure 9) 4140HW combines medium carbon content with highend chromium,Yield strength represents the upper limit of the load that can be safely applied to the metal, which makes it a very important number to know when designing components Elongation Ductility is the capability of the steel to be stretched out without becoming more brittle or weaker in the process


Q Tbn And9gcsh4jzx4y6ywje5vx Xhwku6fuot5vktmkonvv Ore6n6ouwa5 Usqp Cau



Stress Strain Curve For Concrete
Strength of Metals SI Units Strength of Metals Imperial Units Example Strength of Copper at 100 o C As indicated in the first figure the strength of copper is reduced to approximately 95 % at 100 o C With an Ultimate Tensile Strength σ u of 2 MPa for copper the strength is reduced to 095 (2 MPa) = 9 MPaYield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf


Www Asminternational Org Documents 059g Samplechapter Pdf D1a641ad E4e8 7d C565 C9c690c1931e
Also, it is equally interesting to understand the main difference between Tensile Strength and Yield Strength Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstandMaterial Selection Charts In order to demonstrate the power of the material selection chart approach, a number of common property combinations have been plotted these are listed belowIf your browser is capable 1, you should see interactive chart pages which Allow you to view the selection chartsWhy Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange For more information and source, see on this link https//engineeringstackexchangecom


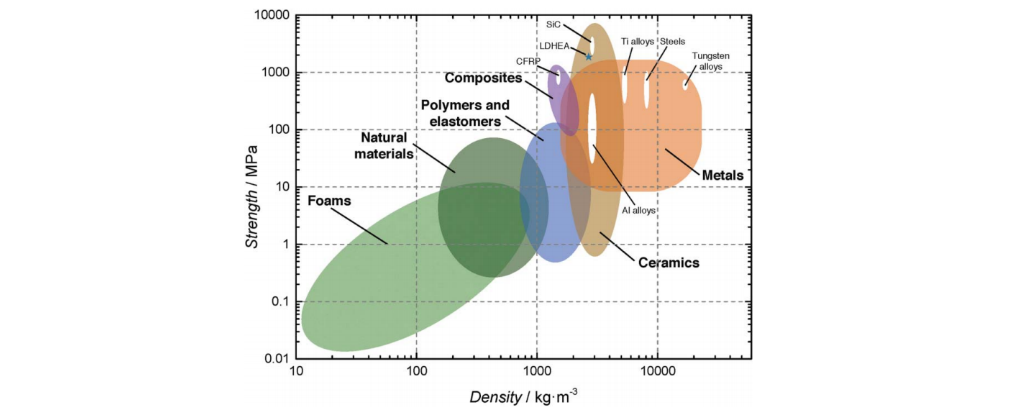
Strength Density
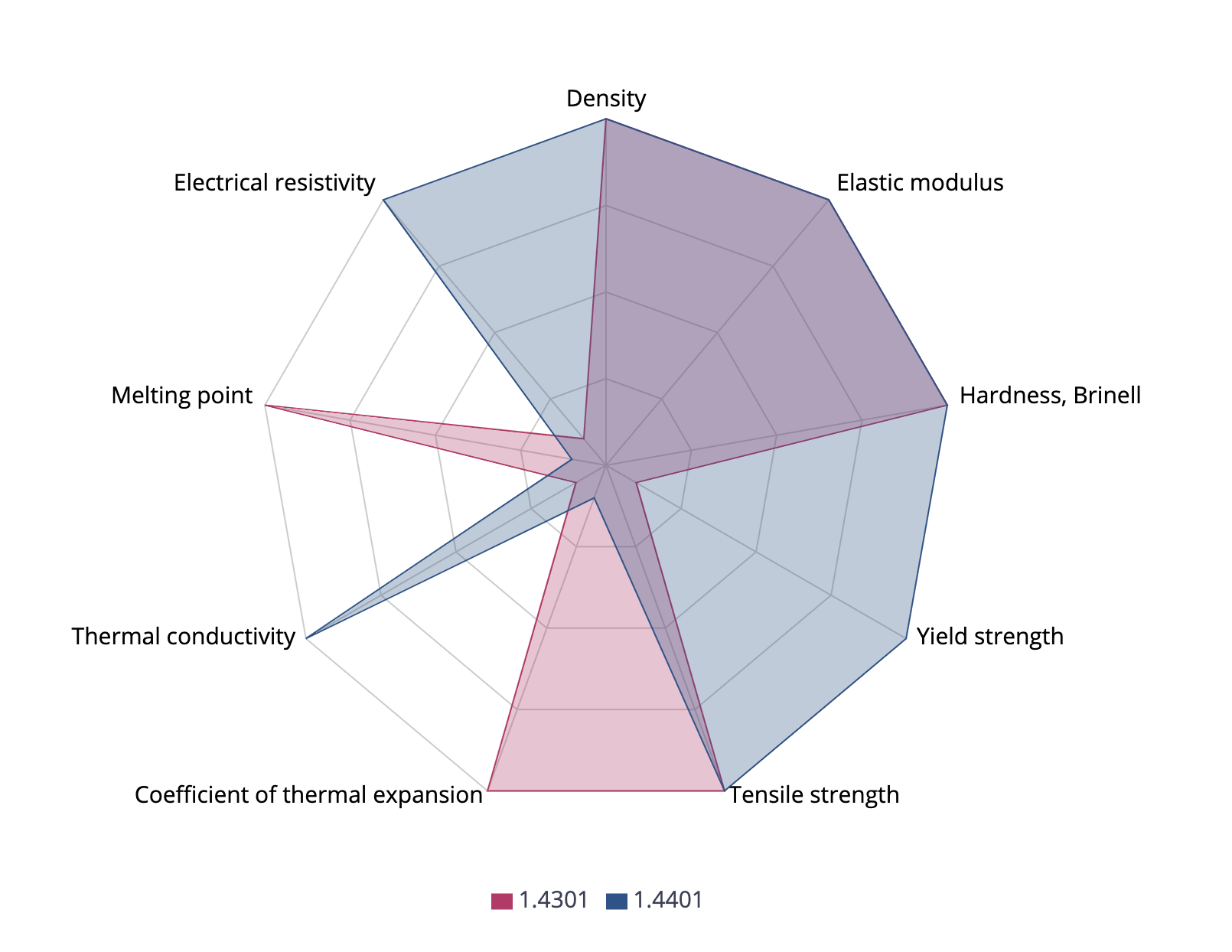


Aisi 304 1 4301 Stainless Steel Matmatch
Whether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirementFor instance, Fig 256 shows a material property chart whereby the limits of specific stiffness (Young's modulus/density) of 300 MN m kg −1 or specific strength (strength/density) of 100 kN m kg −1 have been imposed All materials in the window defined by the limit labelled 'passed region' meet both these constraints, and can beTo find yield strength, the predetermined amount of permanent strain is set along the strain axis of the graph, to the right of the origin (zero) It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point (D) Yield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials


Materials Used In Automotive Manufacture And Material Selection Using Ashby Charts


Strength Density
The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002The chart method is easy when the design of the component specifies a simple objective such as minimizing weight and a single constraint, for instance a specified stiffness, strength, or thermal conductivity (Ashby, 1997a) Perhaps the most significant limitation of this method is that the chart limits decisions in materials selection to onlyYield point is the first point where the specimen yields, where the specimen's crosssectional area begins to contract significantly, or where the strain can increase without increase in the stress Ultimate Tensile Strength σ u Ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress the thermoplastic material can withstand before failing



Material Property Chart An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Material Selection Chart An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The "magnetic field strength" Usually given the symbol H Measured in amps per metre (A/m) The "magnetic flux density" Usually given the symbol B Measured in teslas (or microteslas or gauss) In electromagnetism theory, it is absolutely clear that these are different quantities and you need to be precise about which you are measuringFracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occurs Stiffness is how a component resists elastic deformation when a load is applied Hardness is resistance to localized surface deformation The strength of a material can refer to yield strength, ultimate strength, or fracture strengthStrength vs Density Level 2 Materials Chart Figure 4 Strength vs Relative Cost per Unit Volume Level 2 Materials Chart Strength vs Density Download



What S The Difference Between Critical Load And Yield Stress Physics Stack Exchange


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal
Yield Stress (2% offset)Strength HardeningUltimate Tensile StrengthNeckingFractureTrue Stress 2 Sketch two Stress/Strain Curves on the same graph, making one Curve for a brittle material and one Curve for a ductile material Below the graph, briefly mention in your own words what the key difference is between the two types of materialThe stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002At the yield point, the polymeric material undergoes strong irreversible plastic deformation followed by necking and, in some cases depending on strain rate and temperature Strain hardening is the increase in strength that accompanies plastic deformation beyond the yield point It depends on the network density (physical entanglements and
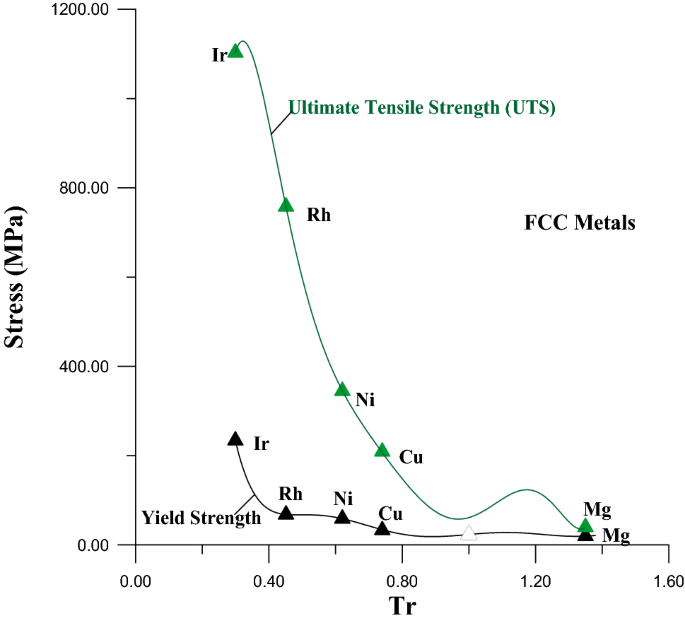


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports


Microstructural Development And Tensile Strength Of An Ecap Deformed Al 4 Wt Cu Alloy
Curve Yield strength is assumed to be the maximum stress observed in each stressstrain diagram and the strain corresponding to the yield strength is the yield strain Stresscontrolled tensiontension fatigue tests were performed at 215 C The ratio of the minimum cyclic stress and the maximum cyclic stress, ie, the Rratio, was 01Strength vs Density Level 2 Materials Chart Figure 4 Strength vs Relative Cost per Unit Volume Level 2 Materials Chart Strength vs Density DownloadChart 1 provides a sample yield curve for July 30, 04 Remember, you can plot yield curves daily because interest rates may change daily In the charts below, we create average yield curves for longer periods, months, or years, and use those to compare the term structure of interest rates for different time periods and to observe trends and



Lecture Slides Chapter 2 Materials Ppt Video Online Download


Www Specialmetals Com Assets Smc Documents Alloys Inconel Inconel Alloy 625 Pdf
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andMaterial Specific Gravity SG Coefficient of Linear Expansion α (m/m K) Maximum Safe Operating Temperature (o C)Thermal Conductivity k (103 cal/(cm sec o C) Tensile Strength


Ocw Mit Edu Courses Materials Science And Engineering 3 11 Mechanics Of Materials Fall 1999 Modules Mit3 11f99 Dn Pdf


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming


Strength Density


Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets


Www Vttresearch Com Sites Default Files Pdf Tiedotteet 1996 T1792 Pdf


Stress Versus Strain
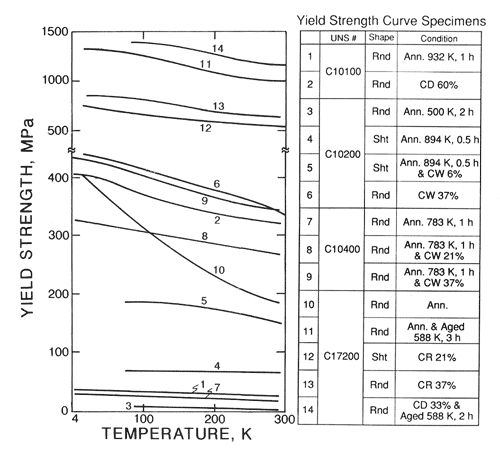


Cryogenic Properties Of Copper


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



New Alloy Is As Light As Aluminum As Strong As Titanium Alloys Nextbigfuture Com



Strength At Break Tensile


Http Userweb Eng Gla Ac Uk Philip Harrison Teaching 09 sandeep pavuluri A materials selection case study Sandeep pavulri 09 Pdf



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Lightweight Flaw Tolerant And Ultrastrong Nanoarchitected Carbon Pnas


Q Tbn And9gcqx7n1txjtekvqqwdc01 Vskeeag6dnpgx03u6nspeqtj9ms3mr Usqp Cau



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Rolling Partial And Full Annealing Of 6061 Characterization Of Microstructure Tensile Strengths And Ductility



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


Plot Of Measured Yield Strength And Square Root Dislocation Density Download Scientific Diagram


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials
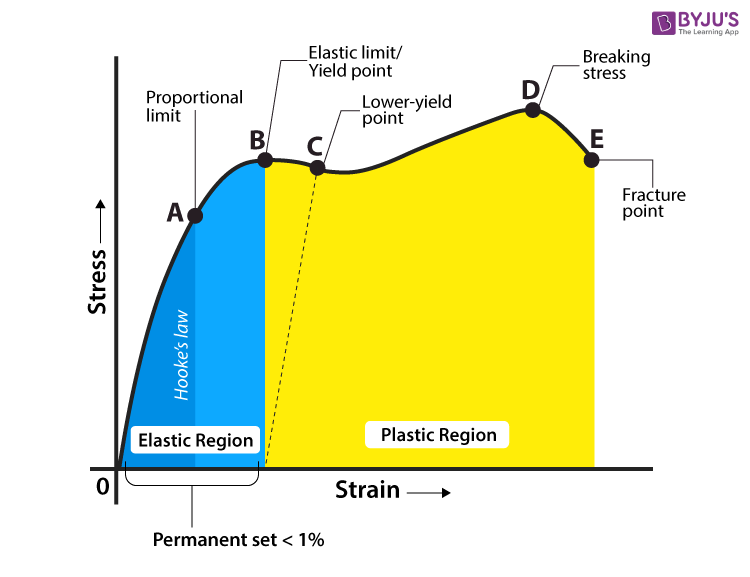


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Composition Properties Ssina



Figure 5 Spark Plasma Sintering Of Metals And Metal Matrix Nanocomposites A Review
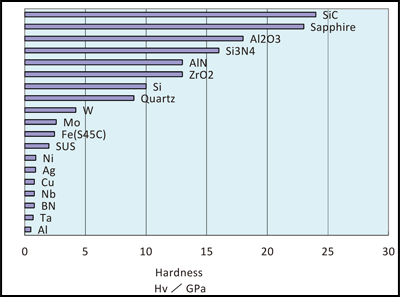


Material Properties And Comparison Charts Ceramics High Melting Point Metals Precision Machining Of Ceramics Quartz Tungsten Molybdenum Top Seiko Co Ltd


Solved 1 Use The Information Presented In The Figure Bel Chegg Com


00mae324 Mpd16



Material Properties Simsolid
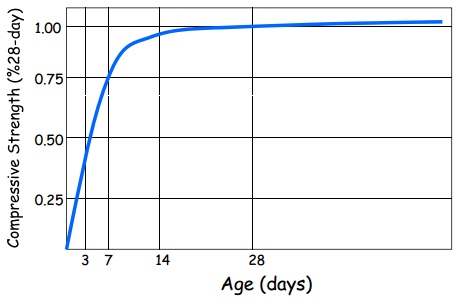


Properties Of Normal Strength Portland Cement Concrete Civilengineeringbible Com



What S The Difference Between Kevlar And Carbon Fiber
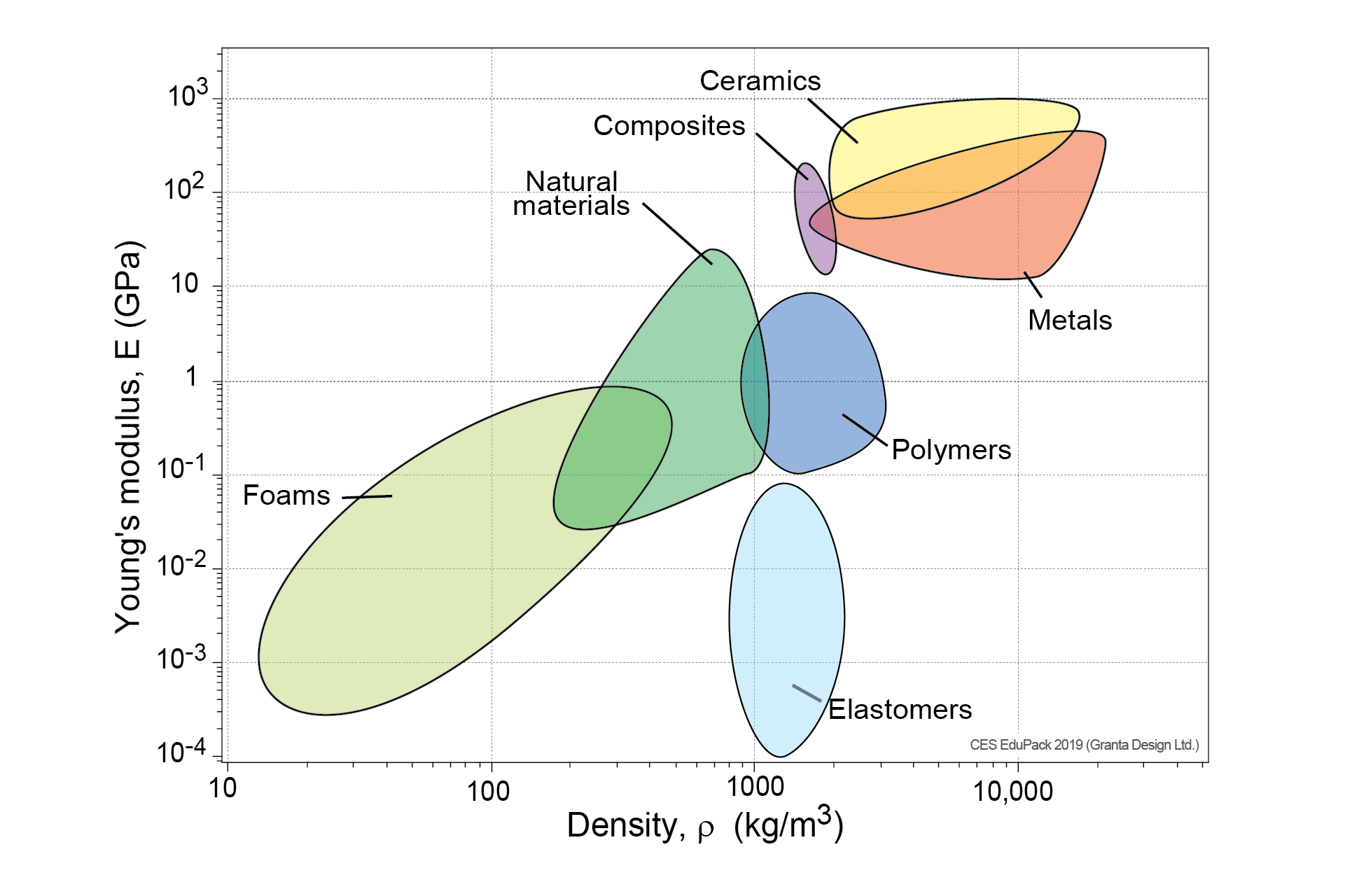


Material Property Charts Granta Design
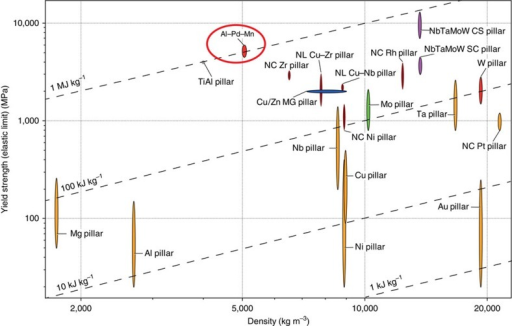


Strength Comparison With Other Metallic And Metallic Gl Open I



D Tensile Machine Operation 1 Click On Datum Shortcut On The Desktop 2 Click On Course Hero
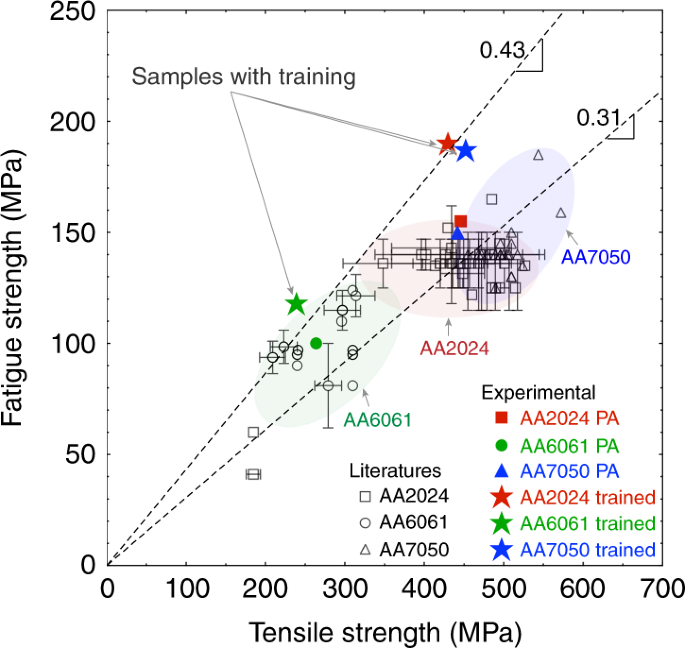


Training High Strength Aluminum Alloys To Withstand Fatigue Nature Communications


Stress Versus Strain



Strength Vs Density Chart For Engineering Materials There Is A Gap In Download Scientific Diagram


390 Materials Design
.jpg)


An Introduction To The Polymer Process And Drawn Fiber


Http Userweb Eng Gla Ac Uk Philip Harrison Teaching 09 sandeep pavuluri A materials selection case study Sandeep pavulri 09 Pdf


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers


Density Curves Video Khan Academy


Materials Selection Bike Dynamo


Mae Ufl Edu Rapidpro Pages 3d printing paper final manuscript Pdf


Esdep Lecture Note Wg2



Material Selection Base Design Considerations The Chair Base Must Be Made Of A Material That Is Durable Strong Stiff And Looks Nice As It Will Draw A Lot Of Attention From The Leather Texture Of The Chair Some Specifications Design Will Be Complex With



If The Density Of A Material Increases Does The Tensile Strength Increase As Well Quora
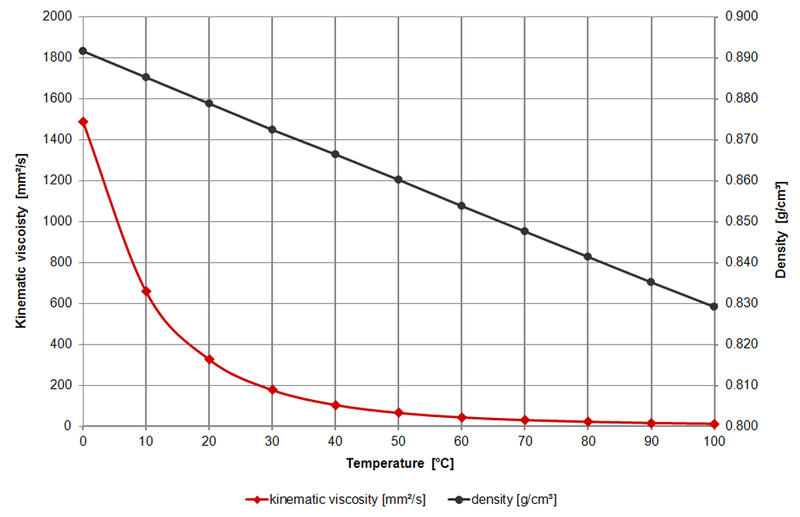


Viscosity Of Engine Oil Viscosity Table And Viscosity Chart Anton Paar Wiki


Metallurgical Materials Science And Alloy Design Mechanical Properties Of Titanium



Materials Selection Of Optimized Titanium Alloys For Aircraft Applications
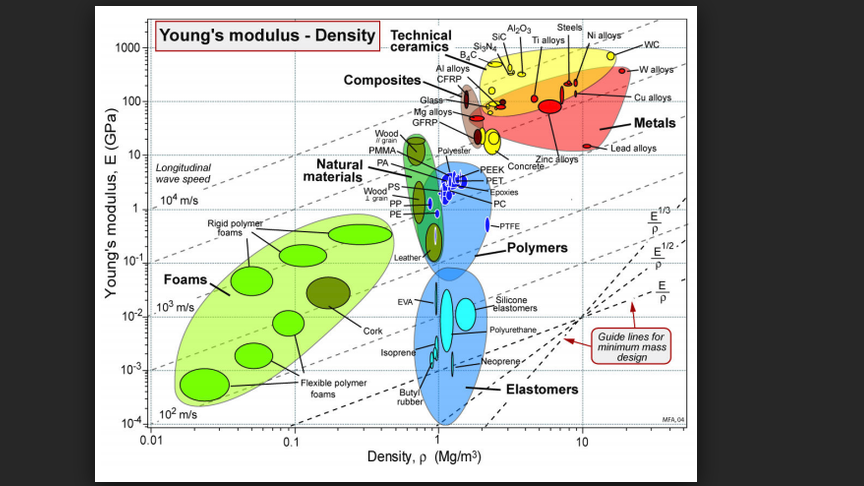


Solved 2 Use The Yield Strength Density Chart Or The Yie Chegg Com
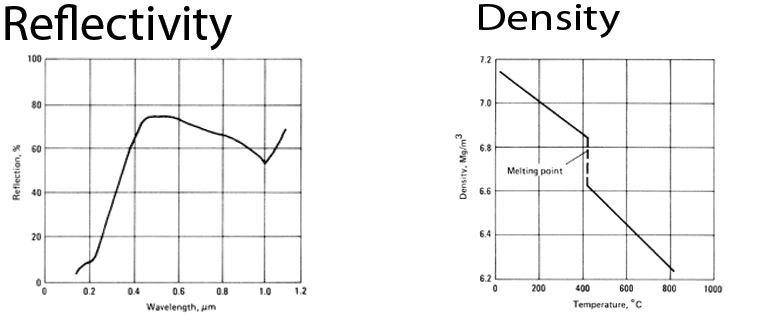


Zinc Metal Properties American Galvanizers Association


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf
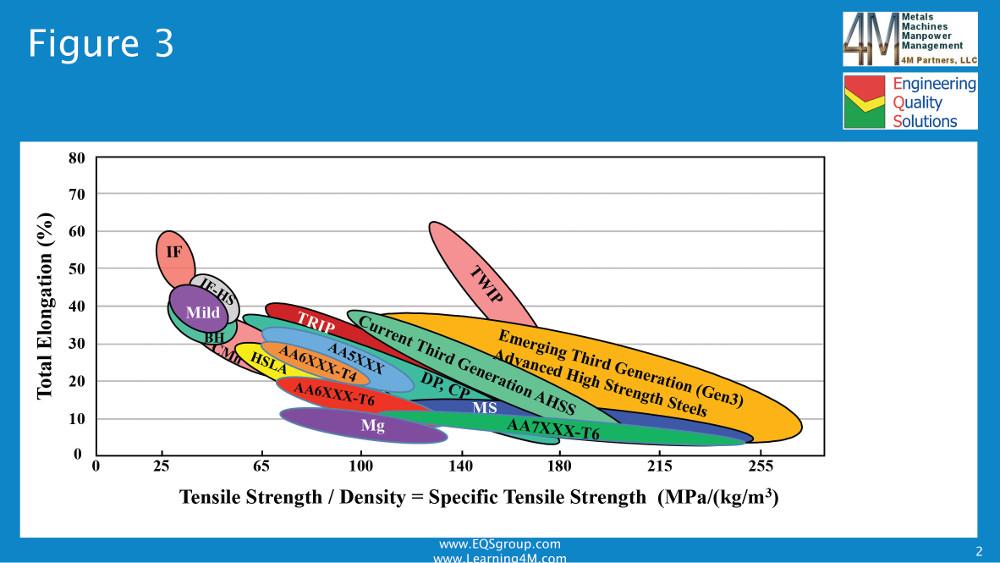


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming
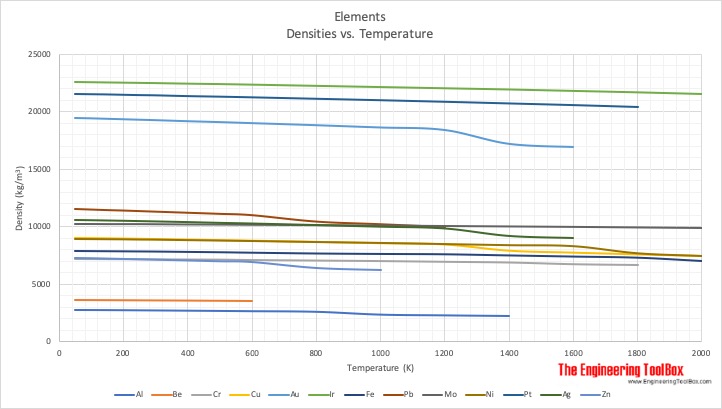


Metals And Alloys Densities
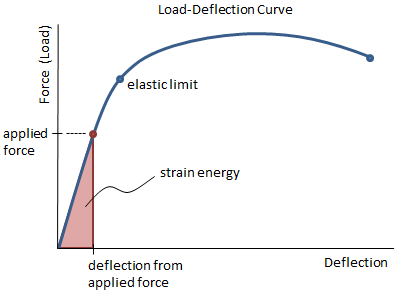


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
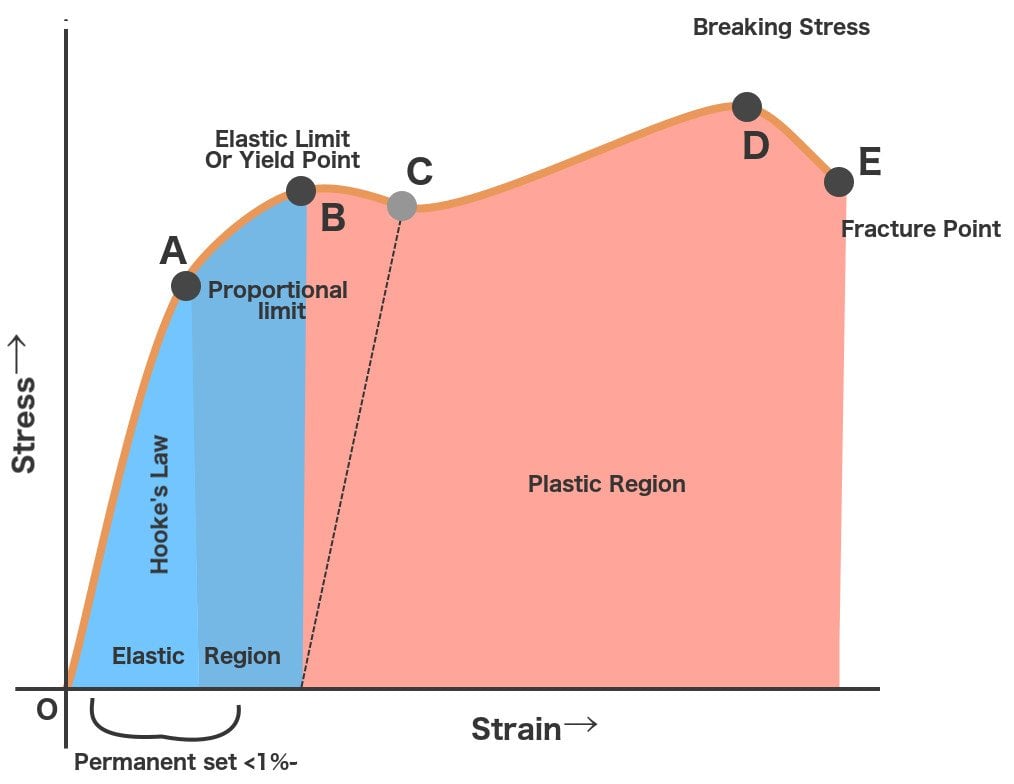


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation


Http Www Dartmouth Edu Cushman Courses Engs171 Wegst Lecture8 Pdf
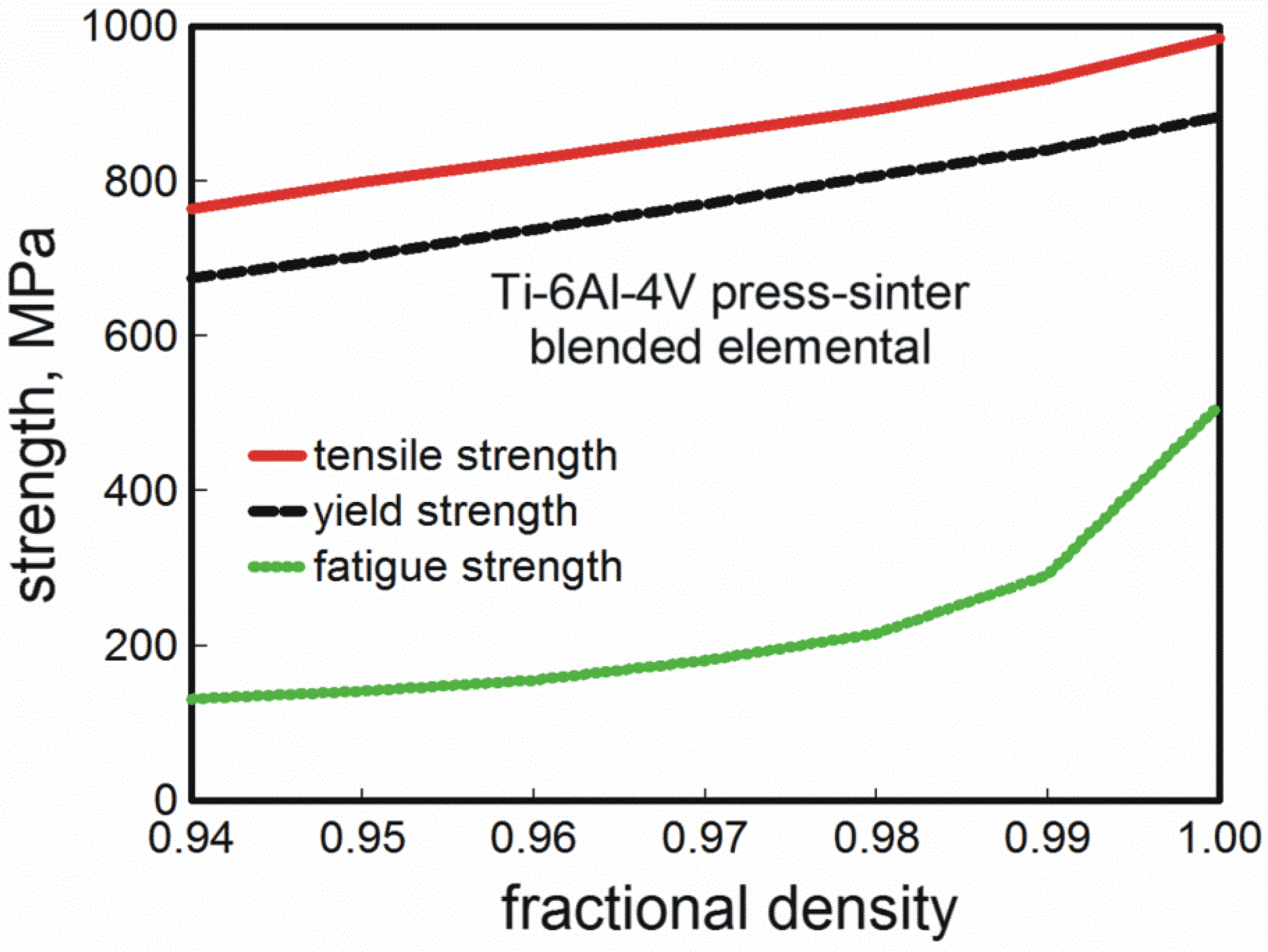


Materials Free Full Text Progress In Titanium Metal Powder Injection Molding Html



Temperature And Strength Of Metals
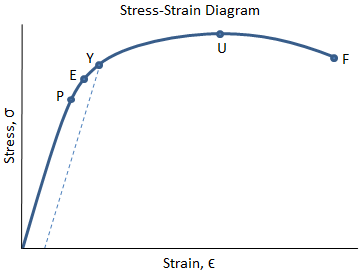


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Ductile Iron Data Section 3 Part 1



Strength Rigidity Hardness What S The Difference Accu



Strength Rigidity Hardness What S The Difference Accu
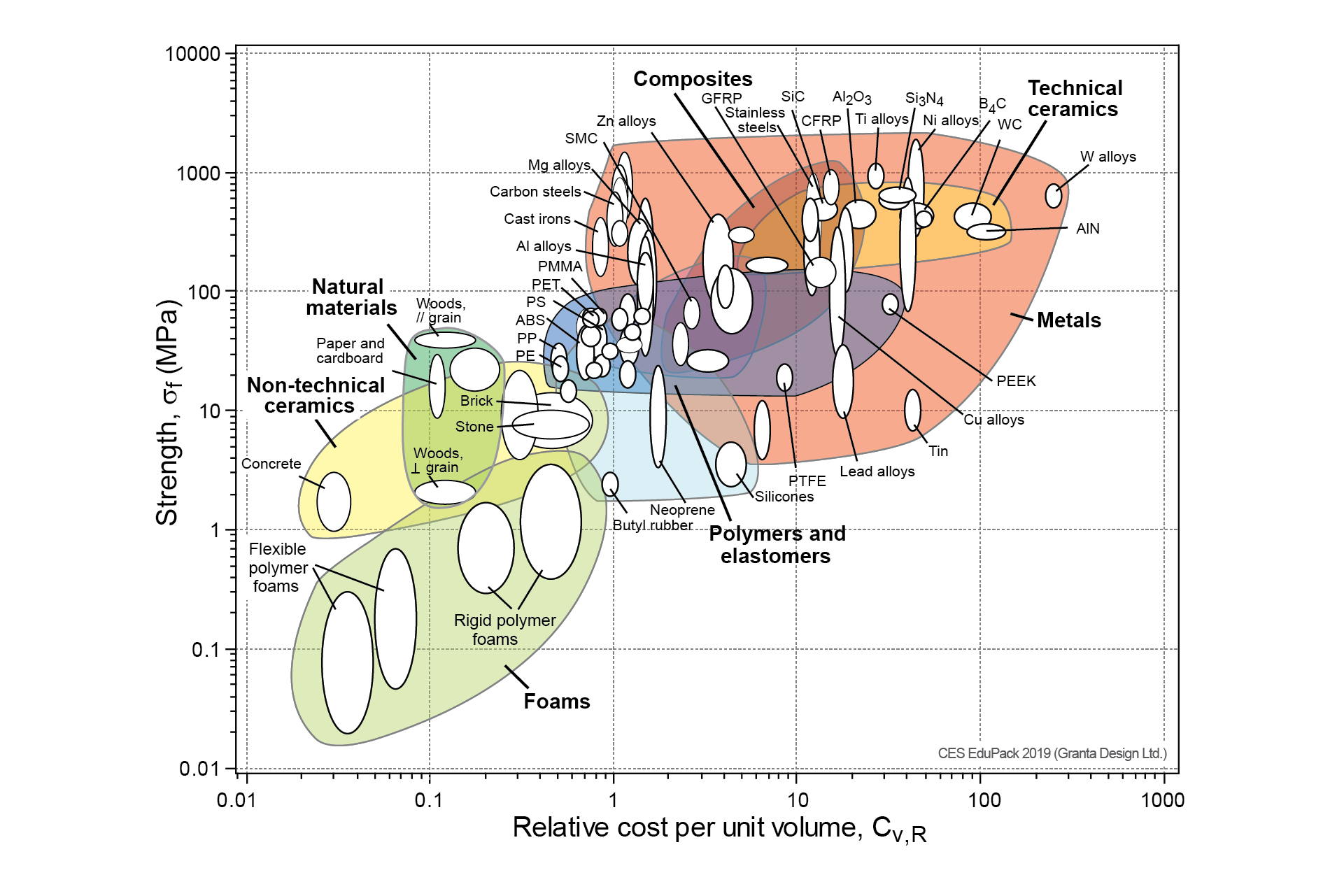


Material Property Charts Granta Design



Density


Http Users Fs Cvut Cz Libor Benes Vyuka Engineeringmaterials 2 Materials Charts 10 Pdf



Young S Modulus Wikipedia



Ultimate Tensile Strength Uts Stress Strain Curve



The Mechanical Properties Of Aluminum Aluminium Guide Com



Yield Strength Of Plastics Basic Principles The Tensile Test And Material Property Table Engineeringclicks



Strength At Break Tensile



Material Property Chart An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Material Property Charts Granta Design


3


Material Property Charts Granta Design



A Non Linear Spring Model For Solid Material Mat Tech



Graphs Of A Relative Yield Strength Vs Relative Density And B Download Scientific Diagram
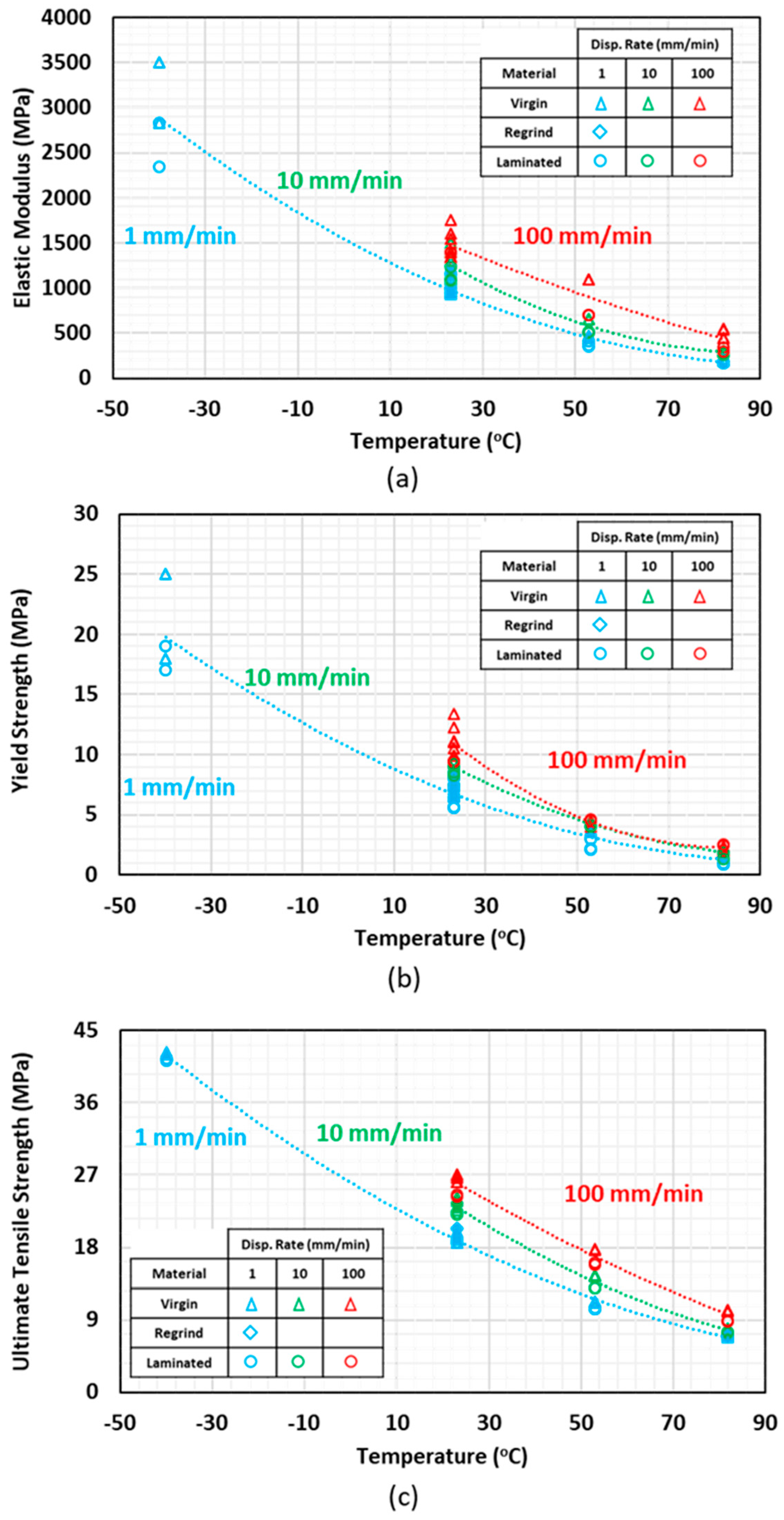


Polymers Free Full Text Tensile Behavior Of High Density Polyethylene Including The Effects Of Processing Technique Thickness Temperature And Strain Rate Html


コメント
コメントを投稿